You’ve probably heard about biofeedback, but you may not know what it is exactly or how it can help you.
Biofeedback therapy helps individuals learn to control their bodies to improve their health. Therapeutic practices typically involve using monitoring devices to provide real-time feedback about bodily activities, such as heart rate, muscle tension, skin temperature, and brainwave patterns. This information is presented to the person training in a visual or auditory format allowing them to learn to regulate the bodily function voluntarily. The goal is to develop greater self-awareness and control over one’s body to produce measurable physical and mental benefits.
Your Brain Controls Your Body and Your Body Controls Your Brain
You know that your brain controls your body, but did you also know that your body controls your brain? It’s a feedback loop that works both ways. The activity in your brain changes moment to moment based on what your body is doing.
Your brain is continuously receiving signals from the rest of your body informing it about the environment and instructing it how to act, think, and feel. Information coming from your senses first gets quickly and subconsciously interpreted by your primitive brain as emotion. Then your higher brain adds a subjective interpretation based on your past experiences to generate thoughts and feelings.
The neural signals coming from your body, telling your brain vital information, like heart rate, breathing, and digestion, are carried by the largest parasympathetic nerve in your body, the vagus nerve. Your vagus nerve starts in the pelvic floor and runs through the entirety of your upper body ending in the brain stem. Your brain, then, interprets and assigns meaning to the signals.
Many physical sensations, like a queasy stomach, tight muscles, or random aches and pains, have an emotional component — which your brain may be correctly or incorrectly adding on. It is an option to become aware of and consciously interpret physical sensations. For example, a gnawing feeling in your stomach could mean that you’re hungry or it could mean you’re anxious about a meeting you have later that day.
You Already Use Biofeedback Unknowingly
Unknowingly, people tend to automatically generate many types of negative biofeedback, especially in the case of depression or anxiety. For example, frowning or scowling expressions, timid or withdrawn postures, and tense tight muscles in your body can increase negative feelings in your brain. Studies show that people with depression have greater muscle tension which increases anxiety and lowers heart rate variability (HRV) which further reinforces the depressive state in the body and brain. HRV is a measure of the variation in time between heartbeats and is directly linked to many aspects of a person’s health. The vagus nerve plays an important role in maintaining physiological homeostasis, which includes reflex pathways that regulate HRV.
You already use your body to alter your brain or to stimulate your vagus nerve in positive ways too. You can also do this intentionally by:
- Splashing cold water on your face
- Using the power of music
- Smiling
- Standing up straight
- Calming your face
- Relaxing your jaw and tongue
- Slowing your breathing
- Clenching and relaxing muscles

Benefits of Biofeedback
Biofeedback therapy can be used to address a variety of health conditions, including:
- Stress management: Research shows biofeedback can help individuals learn how to relax and reduce stress by controlling things like heart rate, muscle tension, and skin conductance.
- Pain management: Studies show that it has been used to help people manage chronic pain conditions by teaching them to control their perception of pain and reduce muscle tension that can exacerbate pain.
- Anxiety and mood disorders: Biofeedback can successfully assist individuals in regulating their physiological responses associated with anxiety, such as increased heart rate or shallow breathing.
Migraines and headaches: Biofeedback can help a person reduce the frequency and intensity of migraines and tension headaches. - Hypertension: Biofeedback can help individuals lower their blood pressure by training them to relax and reduce stress-induced physiological responses.
- Self-regulation: Over time and with repetition, people can learn to voluntarily control what were once thought to be involuntary body processes without the need for constant feedback.
Biofeedback therapy is conducted by trained professionals who tailor the therapy to a person’s specific needs. It can be used as a standalone treatment or in conjunction with other therapeutic methods.
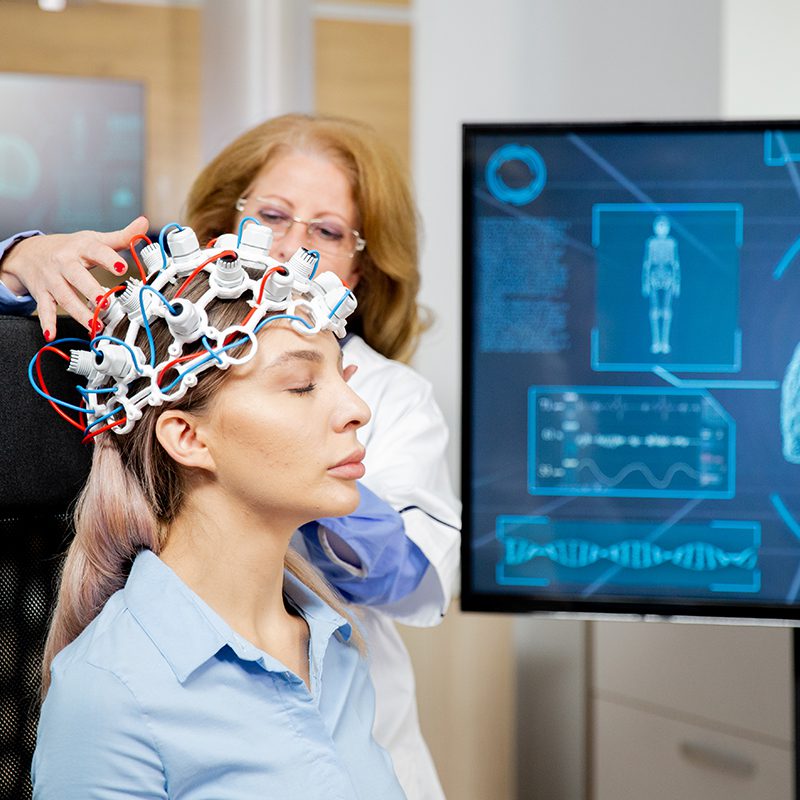
Neurofeedback Is a Form of Biofeedback
Neurofeedback is a form of biofeedback therapy that focuses on regulating brainwave activity through electroencephalography (EEG) technology. It is sometimes referred to as EEG biofeedback or brain training. Unlike traditional biofeedback, which typically focuses on physiological measures like heart rate, breathing, or muscle tension, neurofeedback is specifically designed to help people gain greater control over their brainwave patterns.
Neurofeedback is a non-invasive, painless, drug-free method that actually teaches the brain healthier ways to function. Brain training can optimize brain wave amplitudes, enhance connectivity between parts of the brain, and adjust the level of activity and responsiveness of specific areas of the brain. The brain learns at a subconscious level to create permanent changes that last after training.
Here’s how neurofeedback works:
Assessment
A baseline EEG recording, called a “brain map,” is taken to assess a person’s unique brainwave activity. A brain map is a visual representation of the electrical signals generated by your brain as it operates. It shows, in detail, how different parts of your brain are functioning and communicating with other parts. A map helps identify potential abnormalities or patterns associated with specific neurological or psychological disorders. For example, if someone has excessive beta wave activity, typically associated with anxiety, their brain may be trained to increase calming alpha waves or decrease beta waves.
Feedback
During a training session, electrodes are placed on the scalp and earlobes with conductive paste to monitor brainwave activity. A computer analyzes the data in real time, and teaches your brain to meet preset measures for optimal functioning through cognitive conditioning via positive reinforcement. The reinforcement cues come in various forms, such as listening to music, playing a video game, or watching a movie.
Training
As part of our survival instinct, our brains are always seeking rewards — originally things like food and mating — to ensure the survival of the species. During a neurofeedback session, the brain is given many opportunities to self-correct and be rewarded. When the software reading your brain waves detects activity outside healthy levels, it stops the reward. The music or movie quits playing, a Pac-man stops gobbling dots, or a rocket ship stalls. The reward resumes when your brain starts performing at the desired level again.
Learning and Self-regulation
All learning occurs at a subconscious level. You don’t actually have to “do” anything. With consistent repetition, the brain learns to self-regulate and makes permanent changes to perform more optimally. It will continue to make the adjustments after the training. Because it’s a learning process, the results of neurofeedback occur gradually over time.
Conclusion
At Grey Matters of Carmel, we know how to optimize your brain’s operation to benefit your physical and mental health. Our brain training specialists will map your brain to pinpoint any specific parts not functioning properly. Then, we customize training to alleviate your problematic symptoms.
Neurofeedback has been scientifically shown to help many conditions, including anxiety, depression, autism, ADD/ADHD, concussion, brain injuries, OCD, stroke recovery, PTSD, addictions, trauma, epilepsy, insomnia and sleep disorders, migraines, chronic pain, apraxia, trichotillomania, PANS/PANDAS, brain fog, Parkinson’s, IBS and gut issues, and more. By fine-tuning the brain’s performance, neurofeedback can improve any brain. For example, neurofeedback training could benefit a person’s performance at school, sports, or work.
To find out more about how we can help you, contact us today or call 317-215-7208.
Photo Credits:
Top image: By Allef Vinicius on Unsplash
Second image: By wayhome studio on Freepik
Third image: By DCStudio on Freepik


